Understanding Thixotropy: Properties and Applications
Thixotropy is a time-dependent shear thinning property observed in certain non-Newtonian fluids and gels. Unlike Newtonian fluids, which have a constant viscosity regardless of the applied stress, thixotropic materials exhibit a decrease in viscosity over time when subjected to shear stress. Once the stress is removed, they gradually return to their original, more viscous state. This reversible process is crucial for applications that require dynamic changes in material properties.
Thixotropic Behaviour in Non-Newtonian Fluids
Non-Newtonian fluids exhibit complex behaviours that deviate from the constant viscosity observed in Newtonian fluids like water. Thixotropy is one such behaviour, where the material's viscosity is dependent not just on the current stress but also on the history of applied stress. This means that the fluid’s response can be tailored by varying the duration and intensity of the applied force, allowing for precise control in applications that demand it.
Historical Context and Discovery
The concept of thixotropy has been understood for over a century, first identified in natural clays and gels. Its unique properties were initially harnessed in industries such as ceramics and food production. As scientific understanding grew, the potential applications of thixotropy expanded, leading to its integration into modern engineering practices across a variety of fields.
Thixotropy in Everyday Life
Thixotropic materials are more common in daily life than one might think. Common examples include ketchup, which flows more easily after being shaken, and certain paints that require stirring before application. These materials showcase the practical utility of thixotropy, where controlled application and ease of use are critical.
SoundBounce uses thixotropy to achieve its high-performance noise reduction.
The Thixotropy Effect
The thixotropy effect is characterised by a reversible transition between a liquid-like and a gel-like state. When a thixotropic material is agitated or stressed, it becomes less viscous, allowing it to flow more easily. Once the stress is reduced or removed, the material gradually regains its original viscosity. This behaviour is attributable to the internal microstructure of the material, which temporarily breaks down under stress and reforms when the stress is alleviated.
Microscopic Mechanisms
On a microscopic level, the thixotropy effect is driven by the rearrangement of particles or polymers within the fluid or gel. When stress is applied, these internal structures are disrupted, reducing the viscosity. Once the stress is removed, the structures slowly reassemble, returning the material to its original state. This reversible structural change is what allows thixotropic materials to transition between different viscosities.
Advantages of the Thixotropy Effect
The ability to transition between states offers numerous advantages in practical applications. For instance, thixotropic materials can be easily applied or injected under stress and then solidify to form a stable structure once the stress is removed. This property is particularly beneficial in industries where controlled application and material stability are essential.
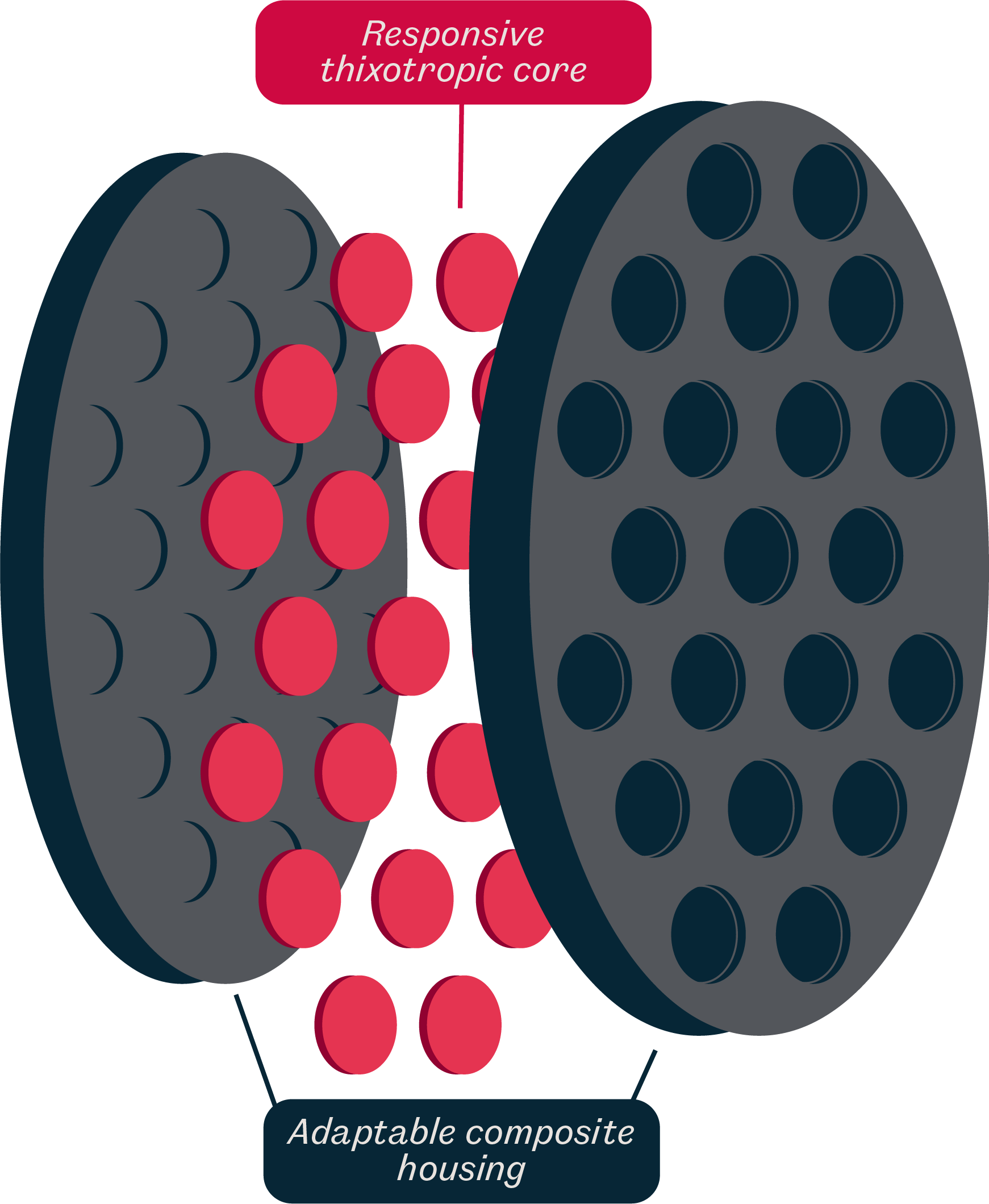
SoundBounce, our novel metamaterial, is stable, non-reactive and adaptable to a multitude of applications across various industries.
Challenges and Considerations
While thixotropy offers many benefits, there are also challenges to consider. The rate of viscosity recovery can be a critical factor in applications where timing is crucial. Additionally, repeated stress and recovery cycles can sometimes lead to fatigue in the material, affecting its long-term performance. Understanding and mitigating these challenges is key to successful implementation.
Our R&D team have spent a decade developing our noise reduction technology.
Properties of Thixotropic Gels
Thixotropic gels are a subset of thixotropic materials that demonstrate significant potential in various applications. These gels are typically composed of a colloidal suspension in which solid particles are dispersed in a liquid medium. The unique properties of thixotropic gels include:
Reversible Viscosity Changes: The ability to transition between states allows for controlled application and adaptability to changing conditions.
Stability: Thixotropic gels maintain their stability over time, ensuring consistent performance in applications.
Self-healing: The reversible nature of thixotropy enables materials to recover from minor damage or deformation, enhancing longevity and reliability.
Composition and Structure
Thixotropic gels are typically composed of a liquid medium with suspended solid particles or polymers. The interaction between these particles is what gives the gel its unique thixotropic properties. Factors such as particle size, concentration, and the nature of the liquid medium can all influence the gel's behaviour, making it possible to tailor these materials for specific applications.
Reversible Viscosity and Stability
One of the defining characteristics of thixotropic gels is their reversible viscosity change. This allows the gel to be easily applied under stress and then maintain its position once the stress is removed. The stability of these gels over time ensures that they remain effective, providing consistent performance in various conditions and environments.
Self-healing Capabilities
Thixotropic gels exhibit self-healing properties, which enable them to recover from minor damage or deformation. This is particularly valuable in applications where durability and reliability are critical. The ability to self-heal extends the lifespan of products and structures, reducing the need for frequent repairs and maintenance.
SoundBounce uses these self-healing properties to ensure a long-life and to minimise depleting efficacy over time.
Applications of Thixotropy
Thixotropic materials are invaluable in numerous industries due to their adaptable properties and practical benefits.
Construction Industry
In the construction sector, thixotropic materials are employed to improve the performance and sustainability of building materials. For example, SoundBounce is used to improve the acoustics of building materials by blocking sound. It can easily be integrated into building materials like insulation and ceiling tiles for enhanced performance.
Enhancing Workability and Sustainability
Thixotropic materials enhance the workability of concrete, allowing for easier placement and finishing. Their use reduces the need for excessive water, which can weaken concrete over time. This not only improves the strength and durability of the structure but also minimises the environmental impact by conserving water resources.
Protective Coatings and Sealants
Thixotropic coatings and sealants offer superior protection against environmental factors such as moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. Their ability to adhere to various surfaces while maintaining flexibility ensures long-lasting protection, reducing maintenance costs and extending the lifespan of structures.
This trait of thixotropy enhances SoundBounce as a sound attenuation material.
Innovative Construction Techniques
The adaptability of thixotropic materials has led to the development of innovative construction techniques. For example, 3D printing of concrete structures can be enhanced using thixotropic formulations, which allow for precise layering and rapid setting. This opens up new possibilities for complex architectural designs and efficient construction processes.
Automotive Design
Thixotropy plays a pivotal role in automotive design, particularly in optimising acoustic solutions. Thixotropic materials can be engineered to provide sound insulation by altering their viscosity in response to mechanical vibrations. This adaptability ensures effective noise reduction without adding significant weight or cost to the vehicle.
Moreover, thixotropic gels are utilised in damping materials to absorb vibrations and enhance passenger comfort. Their ability to adapt to different frequencies and amplitudes makes them a valuable asset in creating quieter, more comfortable vehicles.
This is an application for SoundBounce - to improve the acoustics of motor and electronic vehicles for enhanced passenger comfort.
Noise Reduction and Acoustic Insulation
Thixotropic materials are designed to alter their viscosity in response to mechanical vibrations, providing effective sound insulation. This ability to adapt to various sound frequencies makes them invaluable in reducing noise levels within vehicles, enhancing passenger comfort and driving experience.
It is because of this characteristic that SoundBounce can be altered to target certain frequencies, in particular low frequencies which conventional acoustic materials struggle to damp effectively.
Vibration Damping and Comfort
In addition to noise reduction, thixotropic gels are used in damping materials to absorb vibrations. This helps in minimising the transmission of road vibrations to the vehicle interior, resulting in a smoother and more comfortable ride. The adaptability of these materials allows for effective damping across a range of frequencies and amplitudes.
As well as automotive applications in vibration damping, SoundBounce has been applied to the aerospace industry. We are working with the European Space Agency to qualify our novel material as a fairing acoustic protection, suitable for space flight.
Lightweight Solutions
The ability of thixotropic materials to provide sound and vibration management without significantly increasing the weight of the vehicle is a major advantage. Lightweight solutions contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance, meeting the demands of modern automotive design for sustainability and efficiency.
SoundBounce is 40% lighter and 4x thinner than traditional acoustic solutions.
Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, thixotropic materials are leveraged to address challenges related to heat and noise management. Thixotropic gels are employed in thermal interface materials to improve heat dissipation in compact devices. Their ability to conform to irregular surfaces ensures efficient thermal transfer, preventing overheating and enhancing device performance.
Additionally, thixotropic materials contribute to acoustic management in electronic devices by providing effective sound damping solutions. This ensures an improved user experience through reduced noise levels and enhanced audio quality.
Increased consumer demand for noise cancellation in their headphones can be achieved by SoundBounce in the lightest, most adaptable manner seen yet.
Thermal Management
Thixotropic gels in thermal interface materials (TIMs) enhance heat dissipation in electronic devices. Their ability to conform to uneven surfaces ensures maximum contact and efficient thermal transfer, preventing overheating and improving device reliability. This is crucial in compact devices where space is limited and heat management is challenging.
Acoustic Management
Thixotropic materials play a key role in managing sound within electronic devices. Their ability to dampen vibrations and reduce noise levels enhances the user experience, ensuring clear audio quality and minimising disturbances. This is particularly important in devices such as headphones and earphones, where audio performance is a critical aspect of user satisfaction.
Advancements in Device Design
The integration of thixotropic materials in consumer electronics allows for innovative design solutions. By providing effective heat and noise management without compromising on size or weight, these materials enable the development of more compact, efficient, and high-performing devices. This meets the growing consumer demand for sleek, powerful, and reliable technology.
The Future of Thixotropic Materials
The potential of thixotropic materials extends beyond current applications. As research and development continue, new formulations and innovations are expected to emerge, expanding the possibilities for these versatile materials. Key areas of exploration include:
Advanced Composites: Integrating thixotropic materials into composite structures to enhance mechanical properties and functionality.
Smart Materials: Developing responsive materials that can autonomously adapt to environmental changes, leading to more efficient and sustainable solutions.
Biomedical Applications: Utilising thixotropic gels in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering to improve patient outcomes.
Advanced Composites
Research into integrating thixotropic materials into composite structures aims to enhance their mechanical properties and functionality. These composites could offer improved strength, durability, and adaptability, opening new possibilities in fields such as aerospace and civil engineering, where material performance is paramount.
SoundBounce is a composite material, meaning it combines the power of thixotropy with other material properties for enhanced acoustic performance.
Smart Material Development
The development of smart materials that autonomously adapt to environmental changes is a promising area of exploration. Thixotropic materials, with their inherent ability to respond to stress and recover, are ideal candidates for creating responsive, self-regulating systems that improve efficiency and sustainability in various applications.
Biomedical Innovations
In the biomedical field, thixotropic gels are being explored for use in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Their ability to change viscosity and conform to biological environments makes them suitable for targeted drug delivery and scaffolding in tissue regeneration, potentially transforming patient care and treatment outcomes.
Thixotropy, summarised
Thixotropy is a remarkable property that offers significant advantages across a range of industries. Its ability to adapt to varying conditions and provide reversible changes in viscosity makes it an invaluable asset in construction, automotive design, and consumer electronics. By leveraging the unique properties of thixotropic materials, engineers and product developers can create innovative solutions that enhance performance, sustainability, and user experience.
As the understanding of thixotropy deepens and new applications are discovered, the transformative potential of these materials will continue to drive advancements and address real-world challenges with sustainable and efficient technologies. The future holds exciting possibilities for thixotropic materials, promising to reshape industries and improve the quality of life through smart, adaptable solutions.
Discover SoundBounce’s high-performing capabilities as a sound and vibration dampening material.